Table of Contents
Introduction to the Concept of ERP Systems
Technology is indispensable for driving growth and success in today’s fast-paced and dynamic business environment. One of the most transformative technological solutions that has revolutionized the way organizations operate is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP). This comprehensive and integrated system combines multiple aspects of a business, such as finance, operations, human Resource management, manufacturing, supply chain management, and customer relationship management.

In the highly competitive modern business environment, time is of the essence, and it can make or break the fortunes of a business. By optimizing processes and providing a centralized view of critical business data, ERP enables organizations to make informed decisions and respond quickly, almost in real time, to changing market conditions. ERP-powered companies can grab opportunities quicker than their peers and gain a competitive edge.
What does ERP mean?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a holistic and powerful software suite that helps organizations manage their core business processes more efficiently and effectively. ERP systems provide a centralized platform linked to various departments and functions, allowing for better organizational communication, collaboration, and data sharing.
What can ERP do for businesses?
ERP is binding glue for different business components, irrespective of the type of business structure and scale of the enterprise. It has emerged as a pivotal tool across industries, providing many benefits such as increased efficiency, productivity, collaboration, and decision-making.
For instance, ERP can help optimize the production process, reduce lead times, and improve quality control in the manufacturing sector. In the retail industry, ERP can help manage inventory levels, track sales performance, and provide insights into customer behavior. Similarly, ERP can help streamline service delivery, improve customer satisfaction, and increase profitability in the service sector.
How Does ERP Work?
ERP functions through a centralized database shared across different departments. It utilizes a modular architecture, allowing businesses to select and integrate specific modules tailored to their needs. Data entered into one module automatically updates across the system, ensuring consistency and accuracy in information flow. This interconnectedness eliminates data silos, fostering a holistic view of organizational processes.
ERP systems are a Type of Knowledge Management Systems
Remember, ERP is a specialized knowledge management system (KMS), similar to a Document Management Snd CRM Systems in many ways. Like any other KMS, ERP also captures, stores, and processes vast amounts of organizational data, transforming it into actionable insights. Similarly, information management is at the core of ERP solutions. By consolidating information from various departments, ERP systems facilitate informed decision-making, aiding in strategic planning and resource allocation.
Those interested in knowing more about the broader concept of knowledge management can check my elaborate blog on Knowledge Management Systems on this website.
Critical Components of ERP
Critical components of an ERP system include a centralized database that stores and processes all business data and a suite of modules catering to different functional areas of the organization. ERP modules are flexible and can be customized to cater to specific business requirements, allowing companies a necessary leeway in ERP implementation. The core modules of an ERP solution typically include:

Finance Module:
The Finance module within an ERP system serves as the financial backbone, providing tools for accounting, budgeting, and financial reporting. It centralizes financial data, enabling real-time visibility into cash flow, transactions, and financial performance. This module streamlines invoicing, accounts payable/receivable, and financial planning. By automating these tasks and offering comprehensive analytics, the Finance module empowers decision-makers with accurate financial insights, facilitating better budget allocation and strategic planning.
Marketing Module:
The Marketing module within an ERP system facilitates marketing campaign management, lead tracking, and customer segmentation. It integrates data from various touchpoints, including social media, email campaigns, and website interactions. This module helps analyze customer behavior, preferences, and market trends, enabling personalized marketing strategies. With tools for campaign monitoring, ROI analysis, and customer engagement metrics, the Marketing module empowers organizations to optimize marketing efforts and nurture customer relationships effectively.
Human Resource Management Module:
The Human Resource Management module is integral for managing employee data, payroll, benefits, and performance evaluations. It automates HR processes, including recruitment, onboarding, and training, fostering a streamlined and efficient workforce management system. By centralizing employee information, tracking attendance, and managing compliance, this module ensures HR operations are efficient, compliant, and aligned with organizational goals, contributing to a positive employee experience.
Supply Chain Management Module:
ERP system’s supply chain management module optimizes the pipeline of goods and services from procurement to delivery. It manages inventory levels, tracks shipments, and streamlines supplier relationships. This module enables demand forecasting, inventory optimization, and efficient order fulfillment. Offering visibility into the entire supply chain, including suppliers and logistics, enhances operational efficiency, reduces costs, and ensures timely deliveries.
Operational Management Module:
The Operational Management module optimizes core operational processes, including production scheduling, quality control, and resource allocation. It provides tools for workflow automation, process monitoring, and performance tracking. This module enhances productivity by identifying bottlenecks, improving process efficiency, and ensuring seamless coordination between departments. It contributes to streamlined operations and continuous process improvement.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Module:
The CRM module within an ERP system centralizes customer data, interactions, and sales pipeline management. It tracks customer inquiries, sales opportunities, and service requests, fostering more robust customer relationships. This module enables personalized customer experiences, improves sales forecasting, and drives customer retention strategies by constantly monitoring customer interactions, buying preferences, and purchase history.
Each core module of an ERP system plays a critical role in streamlining operations, enhancing decision-making, and fostering efficiency across different facets of an organization. When integrated seamlessly, these modules collectively contribute to the overall functioning of the ERP system, empowering organizations to achieve operational excellence and drive sustainable growth.
How is ERP Implemented?
The implementation of ERP is a complex process that requires meticulous planning, customization, and integration with existing systems. ERP implementation is multifaceted and demands careful planning and execution across distinct stages. Below, I have accounted for all crucial steps in ERP implementation:

Assessment and Planning:
The initial phase of ERP implementation involves thoroughly assessing the organization’s needs and goals. Conducting a comprehensive analysis of existing processes, identifying pain points, and outlining desired outcomes is crucial. This phase lays the foundation for a well-defined implementation strategy, encompassing timelines, resource allocation, and establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure success.
Selection of ERP Vendor:
Choosing the right ERP vendor aligns closely with the organization’s requirements identified in the assessment phase. It involves researching and evaluating various ERP solutions available in the market. Factors such as scalability, industry-specific functionalities, vendor support, and cost play a significant role in vendor selection. Companies must invite vendor demonstrations, request proposals, and consider user reviews and references before deciding on a suitable vendor.
Customization and Configuration:
Once the ERP vendor is selected, customization and configuration become imperative. Tailoring the system to match specific business processes is vital to maximizing the benefits of ERP. This step involves mapping existing workflows to the ERP system, configuring modules, and potentially developing customizations to address unique business needs. Careful consideration of customization is crucial to avoid overcomplicating the system and ensure seamless integration.
Training and Deployment:
Successful ERP implementation hinges on effective user adoption. Training sessions tailored to different user groups within the organization are essential. Training programs should encompass technical aspects and change management strategies to mitigate resistance to system adoption. To more about various methods of organizational training you can check a blog piece on this website.
Simultaneously, a well-structured deployment plan avoids a disruptive transition from existing mechanisms to the new ERP solution. A phased deployment plan is not a bad idea either, as it could prevent unnecessary hindrances in daily operations due to ERP implementation.
Testing and Optimization:
Testing the configured ERP system is crucial to identify and rectify issues before full-scale deployment. Rigorous testing across scenarios validates system functionality, data accuracy, and integration with existing systems. Post-deployment, continuous optimization is essential. Regularly reviewing processes, gathering user feedback, and addressing any identified inefficiencies or gaps ensures the ERP system evolves in line with the organization’s changing needs.
Companies must remember that ERP implementation is a complex but rewarding process that demands meticulous planning, stakeholder involvement, and a clear roadmap. Following these key steps ensures a structured approach, mitigating risks and maximizing the potential gain from ERP systems for organizations across diverse industries. Success in ERP implementation isn’t merely about installing software; it’s about transforming operations, enhancing efficiency, and driving business growth through strategically integrating technology and processes.
What are ERP Solutions?
ERP solutions refer to the suite of software applications that collectively constitute an ERP system. These solutions are often modular, allowing businesses to pick and choose modules according to their operational requirements. ERP solutions are very flexible and support both onsite and cloud-based deployment.
Examples of ERP Solutions:
Several ERP systems have made significant impacts across industries. Below, I have elaborated on a few standard solutions’ suitability and unique value proposition. Take a read:
SAP ERP:
SAP ERP is a robust, integrated system offering comprehensive functionalities across various business processes. Renowned for its scalability and versatility, SAP caters to large enterprises and mid-sized businesses alike. Its modular structure allows firms to select specific modules like finance, HR, supply chain, and more, making it suitable for diverse industries. SAP’s strength lies in its ability to handle complex operations, offering extensive customization options. However, its implementation can be resource-intensive, making it ideal for organizations seeking a highly customizable solution with intricate business processes and the capability to invest in a longer implementation cycle.
Oracle ERP Cloud:
Oracle ERP Cloud is a scalable, cloud-based solution to streamline business processes. Oracle’s ERP solutions are known for their innovation and modern approach, and they integrate various functionalities, including financial management, procurement, project management, and supply chain operations. It’s suitable for medium to large enterprises aiming for agility, as its cloud-based infrastructure enables quicker deployment and easy scalability. Oracle’s AI and machine learning capabilities set it apart, providing predictive analytics and automation. Its flexibility and user-friendly interface make it an attractive option for businesses seeking modern, adaptable solutions that can grow alongside their operations.
Microsoft Dynamics 365:
Microsoft Dynamics 365 is also a suite of cloud-based applications encompassing CRM and ERP functionalities. It is a very flexible system suitable for businesses of all sizes, particularly those already utilizing Microsoft’s ecosystem. Its strength lies in user-friendliness and interoperability, making it ideal for companies seeking a familiar interface and easy integration with existing Microsoft applications. Dynamics 365 suits businesses looking for an all-in-one solution that prioritizes ease of use and integration within the Microsoft ecosystem.
NetSuite:
NetSuite, acquired by Oracle, is a modern cloud-based ERP solution offering a comprehensive suite of applications covering financial management, CRM, e-commerce, and more. Known for its flexibility and scalability, NetSuite caters to small and mid-sized businesses, particularly those in rapidly growing industries like e-commerce, retail, and professional services. Its cloud-native architecture enables rapid deployment and easy access to real-time data, making it suitable for businesses seeking rapid scalability and accessibility. NetSuite’s unified platform integrates critical business functions, providing a holistic view of operations, making it ideal for companies aiming for quick implementation and growth without requiring extensive IT resources.
Each ERP solution offers distinct advantages, catering to businesses of varying sizes and industries. Understanding their unique features and strengths helps companies to align their specific needs with the most suitable ERP solution for optimal efficiency and growth.
Understanding ERP in the Context of SMEs
SMEs are the backbone of emerging economies as they are decentralized job creators and support often lagard rural economies. Developing the rural and semi-urban segments of the economy through SMEs is crucial for national development, and ERP is emerging as a powerful tool for this cause.
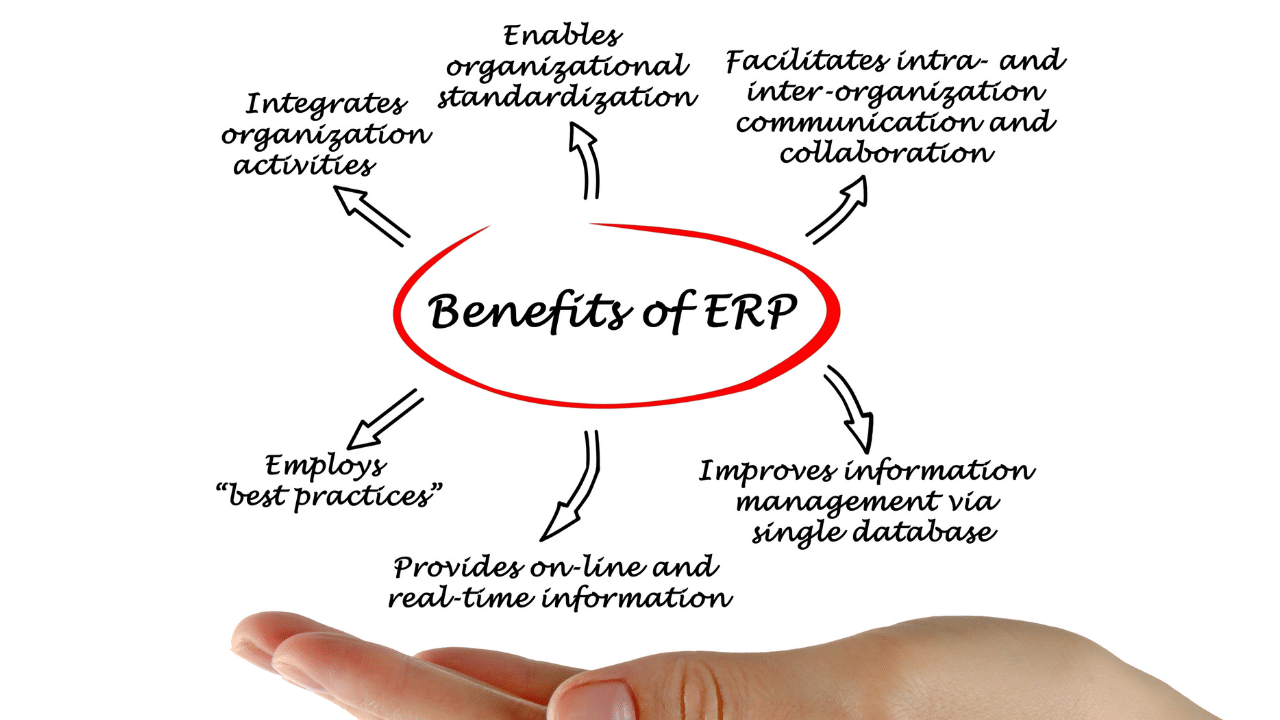
As SME enterprises seek scalable solutions to navigate complexities and drive growth, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is helping them streamline operations and bring cost efficiency, both imperative for success.
Traditionally considered the domain of large corporations due to cost and complexity, ERP solutions have evolved to cater to the needs and constraints of SMEs. Technology and, especially, cloud-based ERP deployment have enabled SMEs to reap the rewards of ERP in business, even on a limited budget.
Listing specific benefits of ERP solutions for SMEs
There are plenty of benefits that ERP systems bring for SMEs. Some of the common benefits are listed below:
Streamlined Operations
Example: A medium-sized manufacturing company struggled with inefficiencies due to disparate systems for inventory management, production, and sales. Implementing an ERP system integrated these processes, providing real-time assessment of inventory levels, demand forecasts, and production schedules. This integration streamlined operations, reduced excess inventory, and optimized production, improving efficiency and cost savings.
Improved Decision-Making
Example: An SME in retail faced challenges in analyzing customer preferences and inventory trends due to fragmented data across various departments. Upon adopting an ERP system, they centralized customer data, sales information, and inventory levels. With comprehensive reports and analytics from the ERP system, they could identify fast-moving products, optimize inventory levels, and tailor marketing strategies, resulting in incremental sales and profits.
Cost Reduction and Resource Optimization
Example: A small service-based company managed different software for accounting, project management, and HR, resulting in increased costs and inefficiencies. Implementing an integrated ERP system streamlined these functions, reducing software licensing fees, eliminating manual data entry, and decreasing operational costs. This optimization allowed them to allocate resources more effectively, improving overall profitability.
Enhanced Scalability and Adaptability
Example: A growing technology startup had multiple standalone software solutions to manage operations. As the company expanded, managing these disparate systems became complex. Adopting a modular ERP system allowed them to add functionalities like CRM, inventory management, and financials as needed. This scalability helped them seamlessly scale their operations while adapting to evolving business needs.
Improved Customer Service
Example: A small e-commerce business needed help processing orders, making timely deliveries, and handling customer inquiries. Implementing an ERP system that integrated order processing, inventory management, and customer support allowed them to automate order tracking, provide accurate delivery estimates, and offer personalized recommendations based on customer buying history, resulting in higher customer satisfaction, leading to customer loyalty and repeat orders.
Future Trends in ERP Solutions
The landscape of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) solutions is on the brink of a significant evolution, propelled by the integration of cutting-edge technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML). These transformative technologies are reshaping the traditional ERP landscape, offering unprecedented opportunities for businesses to optimize operations, enhance decision-making, and drive innovation.

AI and Machine Learning Revolutionizing ERP:
AI and ML are poised to revolutionize ERP systems by enabling predictive analytics, automation, and intelligent decision-making. AI-powered algorithms can analyze gazillion bytes of data to forecast trends, anticipate demand, and optimize inventory levels. Machine learning algorithms learn from historical data, continuously improving processes and recommending more efficient workflows. These capabilities empower ERP systems to provide actionable insights, automate routine tasks, and adapt dynamically to changing business needs.
Impact on SMEs and Small Businesses:
Integrating AI and ML in ERP solutions holds immense promise for SMEs and small businesses. These technological advancements offer cost-effective solutions that were previously inaccessible to smaller enterprises. AI-driven ERP systems allow SMEs to leverage predictive analytics for demand forecasting, optimize inventory management, and personalize customer experiences. Automating repetitive tasks reduces manual workload, allowing SMEs to focus on innovation and strategic initiatives. Furthermore, the scalability and flexibility of AI-enabled ERP solutions cater to the evolving needs of growing businesses without substantial upfront investments.
Implementation Challenges and Opportunities:
Implementing AI and ML in ERP systems introduces challenges related to data quality, system integration, and the need for skilled resources. However, the potential advantages far exceed the challenges. Forward-thinking organizations embrace AI-powered ERP solutions, recognizing them as strategic investments that drive operational efficiency and competitive advantage. Moreover, the trend towards cloud-based ERP solutions facilitates easier adoption of AI and ML capabilities, enabling businesses to access cutting-edge technologies without significant infrastructure costs.
Conclusion:
Enterprise Resource Planning systems have become must-have tools for businesses seeking operational efficiency, streamlined processes, and informed decision-making. Their integration capabilities, data centralization, and ability to adapt to changing business landscapes make them pivotal in today’s competitive environment. As technology advances, ERP’s role in driving business success is poised to expand, shaping the future of organizational management.
The future of ERP solutions lies in harnessing the full potential of AI and ML. As these technologies continue to evolve, ERP systems will become more intuitive, adaptive, and capable of delivering actionable insights in real-time. From predictive maintenance in manufacturing to personalized customer service in retail, AI-powered ERP solutions will redefine how businesses operate and innovate.
Furthermore, Integrating AI and ML in ERP solutions heralds a new era of efficiency, agility, and growth. Particularly for SMEs and small businesses, these technologies present a game-changing opportunity to level the playing field and compete on a larger scale. Embracing these advancements in ERP systems is not merely an upgrade but a complete transformation for businesses, irrespective of their size and scale.
Kartikay Ungrish is the Founder-director of Worthy Education Academy & Worthy Financial Services. He is a UGC NET-qualified Assistant Professor of Management, A MBA, a licenced mutual fund distributor, and a financial advisor. He helps people build wealth through prudent investments in mutual funds and other financial products. Start by creating your free wealth management account with him as your financial advisor. Contact for more details.














